
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the Hefei Cancer Hospital of CAS, has developed a new method to accurately measure hemoglobin levels in blood using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS).
Their study, published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, demonstrates how this method can greatly improve the reliability and precision of NIRS-based blood analysis.
NIRS is valued for its convenience, non-invasiveness, and sensitivity. However, in whole-blood testing, the weak absorption features of hemoglobin (Hb) are often masked by strong water absorption, sample scattering, and instrument noise, which limits quantitative accuracy.
To address this issue, the researchers developed an integrated processing and feature retrieval method that combines Wavelet Packet–Fuzzy Shrinkage denoising (WPT-FS) with the Whale Optimization Algorithm.
"We use the 'fuzzy shrinkage' technique to remove noise from the signal, and the whale optimization algorithm to identify the key parts of the signal that show hemoglobin," said Prof. HAN Xin, who led the team.
This approach first applies an adaptive "fuzzy shrinkage" threshold function to remove noise across multiple scales while preserving meaningful spectral information. Then, using swarm intelligence, the algorithm searches for optimal feature node combinations in the high-dimensional node space to reconstruct Hb-rich spectral features. Finally, partial least squares (PLS) modeling is used to complete the quantitative analysis.
When tested on 106 whole-blood samples, the method significantly reduced background noise, achieving a root mean square error of prediction of 2.0409 and a prediction coefficient of determination (R²_P) of 0.9746.
Further data augmentation experiments also confirmed the model’s robustness under more heterogeneous data distributions, achieving an average percentage error of about 1.7%.
This study provides a reliable tool for non-invasive and accurate blood analysis, and could support future medical diagnostics and health monitoring.
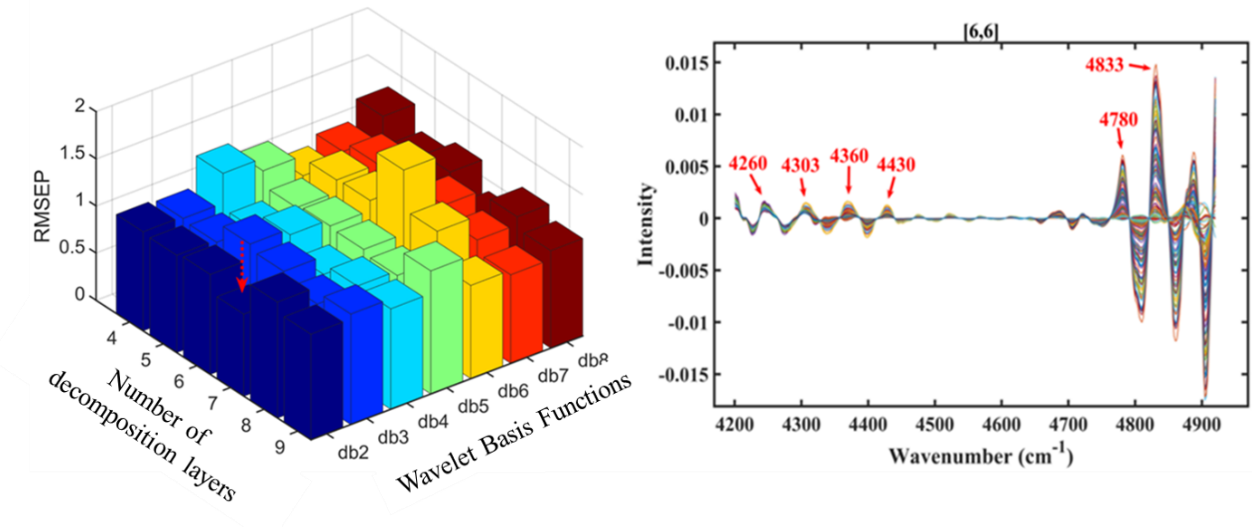
Core parameter determination and Hb-related node reconstruction results (Image by HAN Xin)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

